Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Teshigawara, Makoto; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kinsho, Michikazu; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2021-022, 208 Pages, 2022/02
The Materials and Life science experimental Facility (MLF) is an accelerator driven pulsed spallation neutron and muon source with a 1 MW proton beam. The construction began in 2004, and we started beam operation in 2008. Although problems such as exudation of cooling water from the target container have occurred, as of April 2021, the proton beam power has reached up to 700 kW gradually, and stable operation is being performed. In recent years, the operation experience of the rated 1 MW has been steadily accumulated. Several issues such as the durability of the target container have been revealed according to the increase in the operation time. Aiming at making a further improvement of MLF, we summarized the current status of achievements for the design values, such as accelerator technology (LINAC and RCS), neutron and muon source technology, beam transportation of these particles, detection technology, and neutron and muon instruments. Based on the analysis of the current status, we tried to extract improvement points for upgrade of MLF. Through these works, we will raise new proposals that promote the upgrade of MLF, attracting young people. We would like to lead to the further success of researchers and engineers who will lead the next generation.
Rodriguez, D.; Abbas, K.*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Nonneman, S.*; Rossi, F.; Takahashi, Tone
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1014, p.165685_1 - 165685_10, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:57.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nishimura, Akihiko; Furusawa, Akinori; Takenaka, Yusuke*
AIP Conference Proceedings 2033, p.080002_1 - 080002_5, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Green & Sustainable Science & Technology)We developed a cpmpact laser maintenance device in order to access a 23 mm diameter for heat exchanger tubes of nuclear power plants. A laser instrumentation device was desighned and assembled to measure the corrosion depth at the inlet of heat exchanger tubes. This device can be applied for heat exchanger tubes in CSP where erosion or cracking might be caused by repetitive thermal induced stress.
Hiroi, Kosuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Su, Y. H.; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi
JAEA-Technology 2016-021, 14 Pages, 2016/10
Energy resolved neutron imaging techniques have been developed at BL22 "RADEN" installed in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of J-PARC. A polarized neutron imaging technique attracts much attention as a magnetic imaging method that enables to obtain a quantitative magnetic field distribution in an industrial product under driving state. At RADEN, a polarization analysis apparatus for polarized neutron imaging experiments has been prepared, but its performance was not fully achieved due to imperfectness of the field connection between devices. To improve the performance of polarization analysis system at RADEN, we performed magnetic field simulation of this system, and optimized the magnetic field environment by evaluating the magnetic field connection. After the optimization, we rearranged devices of the system, and confirmed that uniform polarization distribution could be obtained within 4 4 cm
4 cm field of view.
field of view.
Yamamoto, Tsuyoshi; Hashimoto, Yasunori*; Kitazawa, Sin-iti; Yatsuka, Eiichi; Hatae, Takaki; Sugie, Tatsuo; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Takeuchi, Masaki; Kawano, Yasunori; Itami, Kiyoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 96-97, p.1012 - 1016, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan Domestic Agency (JADA) is responsible for six diagnostic systems in the ITER project. We have successfully developed an instrumentation and control (I&C) system for the diagnostic systems. The I&C system manages internal operations for measurement such as health checks of sensors, configuration of measurement parameters, and consistency checks between measurement parameters. We developed a conversion tool to convert operational flowcharts to EPICS records. The sequencing management function coordinates the execution of operation steps by monitoring changes in the record values. It was designed so that the relationship between the records and steps is determined automatically according to the flowcharts as much as possible. We validated the performance of the I&C system for the thermocouple measurement system, and are continuing the development of even more complex I&C systems for other JADA diagnostic systems.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Takeda, Takeshi; Asaka, Hideaki; Nakamura, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 43(1), p.55 - 64, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)Effects of non-condensable gas from the accumulator tanks on secondary depressurization, as one of accident management (AM) measures in case of high pressure injection system failure, are studied at the ROSA-V/LSTF experiments simulating a ten instrument-tube break LOCA at the PWR vessel bottom. In an experiment with no gas inflow, the secondary depressurization at -55 K/h initiated by SI signal with 10 minutes delay succeeded in the LPI actuation. On the other hand, the gas inflow in another experiment degraded the primary depressurization and resulted in core uncovery before the LPI start. The third experiment with rapid secondary depressurization and continuous auxiliary feedwater supply, however, showed a possibility of long-term core cooling by the LPI actuation. RELAP5/MOD3 code analyses well predicted these experiment results and clarified that condensation heat transfer was largely degraded by the gas in the U-tubes. In addition, a primary pressure - coolant mass map was found to be useful for indication of key plant parameters of AM measures.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Takeda, Takeshi; Asaka, Hideaki; Nakamura, Hideo
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2005-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu, Vol.3, p.223 - 224, 2005/09
Shown below are experimental results on characteristics of reactor instrumentations including a coolant mass tracking method and core exit thermocouples (CETs) which are necessary to precise operator actions for accident management (AM) during a loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) at a pressurized water reactor (PWR). The experiments at the ROSA-V/LSTF facility of the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute simulated small break LOCAs at the PWR vessel bottom and clarified effects of secondary depressurization as one of the AM measures in case of high pressure injection system failure and non-condensable gas inflow from the accumulator injection system. It was shown that the coolant mass tracking method based on three types of water level instruments could detect most of the primary coolant mass change between the initial state and core-heatup starting condition. The CET characteristics to detect the core heatup conditions were significantly degraded by the condensed water fall-back during the secondary depressurization action.
 March 31, 2005
March 31, 2005Department of Health Physics; Safety Division, Naka; Safety Division, Takasaki; Radiation Control Division, Oarai; Safety Division, Kansai; Operation Safety Administration Division, Mutsu
JAERI-Review 2005-028, 232 Pages, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Takeda, Takeshi; Asaka, Hideaki; Nakamura, Hideo
JAERI-Research 2005-014, 170 Pages, 2005/06
A small break LOCA (SBLOCA) experiment was conducted at the LSTF of ROSA-V program to study effects of accident management (AM) on core cooling, which is important in case of high pressure injection (HPI) system failure during an SBLOCA at a PWR. The experiment, SB-PV-03, simulated ten instrument-tube break LOCA at the PWR vessel bottom equivalent to 0.2% cold leg break, total HPI failure, non-condensable gas inflow from accumulator injection system (AIS) and AM actions on secondary depressurization at -55 K/h and auxiliary feedwater (AFW) supply for 30 minutes. It was clarified that the AM actions were effective on primary depressurization until AIS injection end at 1.6 MPa, but thereafter became less effective by the gas inflow, resulting in low pressure injection (LPI) delay and whole core heatup under continuous water discharge at the break. The report describes these phenomena including core heatup related with primary coolant mass and AM actions, primary-to-secondary heat transfer analysis and estimation of gas in the primary loops.
 March 31, 2004
March 31, 2004Department of Health Physics; Safety Division, Naka; Safety Division, Takasaki; Radiation Control Division, Oarai; Safety Division, Kansai; Operation Safety Administration Division, Mutsu
JAERI-Review 2004-024, 209 Pages, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Shimizu, Shigeru; Zhang, Q.; Kajimoto, Yoichi; Kawasaki, Tomokatsu; Fujii, Katsutoshi
JAERI-Tech 2003-095, 52 Pages, 2004/01
The International Standards ISO4037-1 of the International Organization for Standardization widely applied in the world to construct X-ray reference fields for performance tests of radiation measuring instruments. The application of the current JAERI's X-ray reference field constructed in accordance with the Japanese Standards should be limited for domestic purposes becase of the characterization technique different from the International Standards. Therefore,for application to international performance tests, X-ray reference fields in the narrow,wide and high air-kerma series based on the International Standards were established using the medium-hard X-ray generator of the Facility of Radiation Standards(FRS), JAERI. This report presents quality characterization, estimation of X-ray spectra of each dose units of the new FRS's fields,and comparison of the qualities and the X-ray spectra to those of the ISO's. The FRS's qualities show good agreement with ISO's: the reference fields should serve for performance tests for international radiation protection purposes.
 March 31, 2003
March 31, 2003Department of Health Physics; Safety Division, Naka; Safety Division, Takasaki; Radiation Control Division, Oarai; Safety Division, Kansai; Operation Safety Administration Division, Mutsu
JAERI-Review 2003-034, 208 Pages, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Kaoru; Tamura, Itaru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Arai, Masatoshi; Middendorf, H. D.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 1, p.351 - 354, 2003/07
In this research report we describe the design of DYANA, a new neutron spectrometer dedicated for biology, biomaterials, and related soft-matter studies, which will be installed in the material and life science experimental facility project at the JAERI Tokai establishment. The DYANA spectrometer is an indirect-geometry crystal-analyzer instrument and its energy and momentum transfer range are from several 10 eV to several meV and from 0.1
eV to several meV and from 0.1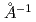 to several
to several 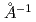 , respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
, respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
JMTR Pressure Measurement Pipe Investigation Committee
JAERI-Review 2003-014, 117 Pages, 2003/03
On December 10、2002, the leak was found at the pressure measurement pipe attached to the exit pipe of No.1 filing pump of the refining system of a primary cooling system at JMTR in Oarai Research establishment JAERI. Investigation Committee for Water Leakage from Instrumentation Pipe in JMTR was established and organized by specialists from inside and outside JAERI on December 16 and its meeting was held in public 3 times by 6th January, 2003. They investigated the cause and countermeasures of cracks, and also investigated enhancement of safety management. This is the report on the cause and countermeasures of cracks and enhancement of safety management.
Shibata, Kaoru; Tamura, Itaru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Arai, Masatoshi; Niimura, Nobuo
JAERI-Research 2002-036, 30 Pages, 2003/03
In this research report we describe the design of DYANA, a new neutron spectrometer dedicated for biology, biomaterials, and related soft-matter studies, which will be installed in the material and life science experimental facility project at the JAERI Tokai establishment. The DYANA spectrometer is an indirect-geometry crystal-analyzer instrument and it's energy and momentum transfer range are from several 10 eV to several meV and from 0.1
eV to several meV and from 0.1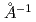 to several
to several 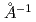 , respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
, respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
Saito, Yoko; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Usuda, Shigekazu
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 255(2), p.341 - 345, 2003/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.64(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Department of Health Physics; Safety Division, Naka; Safety Division, Takasaki; Radiation Control Division, Oarai; Safety Division, Kansai; Operation Safety Administration Division, Mutsu
JAERI-Review 2002-036, 219 Pages, 2002/12
no abstracts in English
Komori, Yoshihiro; Matsui, Yoshinori; Itabashi, Yukio; Yamaura, Takayuki; Nagao, Yoshiharu
KAERI/GP-195/2002, p.59 - 69, 2002/00
JAERI has been developing irradiation technique and facilities for irradiation tests in the JMTR to improve irradiation capability keeping up with progress of nuclear fuels and materials research. This paper summarizes recent development on irradiation technique for the JMTR. Design study and installation of the IASCC (Irradiation Assisted Stress Corrosion Cracking) irradiation test facility was main and the most urgent task of the field in the last five years since two large projects for IASCC were planned in Japan to start irradiation tests in 2002. Almost four years were devoted to preliminary design study, detail design and installation of the facility, then IASCC irradiation test started in March, 2002. Instrumentation technique and capsules development for other research purposes also have been steadily progressing during the term, and new type of off-line temperature monitor, dual re-instrumentation device and the uniform irradiation capsule became available for the irradiation tests.
Department of Health Physics; Safety Division, Naka; Safety Division, Takasaki; Radiation Control Division, Oarai; Safety Division, Kansai; Operation Safety Administration Division, Mutsu
JAERI-Review 2001-041, 221 Pages, 2001/12
no abstracts in English
HTTR Utilization Research Committee
JAERI-Review 2001-016, 232 Pages, 2001/05
no abstracts in English